Whether you’re a VoIP user or not, you’ve probably experienced one-way audio during a phone call. While VoIP offers businesses many benefits and modern capabilities, it’s normal to experience audio issues periodically. So, in this article, we’ll go over how to troubleshoot one-way audio. This way, you can solve this issue as quickly as it appears.
What is One-Way Audio?
One-way audio happens when the receiver can’t hear you, but you can hear them (or vice versa). It’s a common VoIP issue that impacts your ability to communicate during a call. And one-way audio often leads to a constant exchange of “Hello?” and “Can you hear me now?” – which is frustrating for both parties on the line.
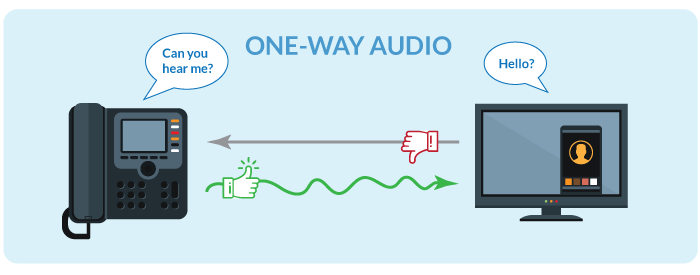
Why Does It Occur?
It’s possible for one-way audio to occur during the beginning or middle of an existing call. Disruptions to the audio stream cause this issue and appear for a number of reasons.
The most common causes include:
- Equipment issues
- Firewalls / NAT blocking voice data
- Incompatible codecs
- Routing misconfiguration
We will look at each of these one-way audio causes and explain how to troubleshoot them.
How to Troubleshoot One-Way Audio: 4 Tips
Although one-way audio is a typical issue among VoIP calls, it is usually easy to diagnose and fix. Let’s look at how to troubleshoot one-way audio.
1. Check Your Equipment
Faulty equipment leads to many VoIP call quality issues, including one-way audio. So, the best way to start troubleshooting one-way audio is to rule out your equipment as the cause.
Equipment Issue Solution
Verify that all your equipment (headset, microphone, and desk phones) is properly connected by checking all cables and selected inputs on your devices. Then, inspect your hardware for any visible damage.
Once you’ve assessed your equipment’s physical condition, test your line. For all setups (softphones, IP phones, and legacy phones), simply initiate a test call and see if you can hear audio on both ends. If you’re using a softphone, you can also use any audio recording software to ensure your inputs are correctly configured.
2. Review Your Router’s Settings
Voice over IP uses packet switching technology to deliver calls through the internet. So, in order for these calls to succeed, voice data must travel from one point to another. This means these data packets must pass through your network’s firewalls – which can block audio packets from transmitting to their destination.
It’s worth noting that Network Address Translation (NAT) acts as a firewall and may also be causing one-way audio.
Firewalls / NAT Blocking Voice Data Solution
To troubleshoot this type of one-way audio issue, make sure the firewall ports are open to your provider’s recommended settings. For United World Telecom users, open ports 10,000 to 60,000. Additionally, whitelist your provider’s IP address in your firewall’s settings.
If that doesn’t work, the problem may lie with NAT. First, evaluate your network. Do you have more than one router supplying NAT? If so, you may be double NATing your traffic – leading to data arriving at the wrong destination. The best way to fix this is to turn off the extra instances of NAT.
After that, if you’re still experiencing one-way audio, try equipping SIP ALG. This network component allows your call data to pass through your firewall’s security checks and NAT rules. However, it’s critical to note that if SIP ALG is implemented incorrectly, it will lead to other problems, which is why most providers recommend leaving it off.
Depending on your setup, you may need to work with your provider to understand the best method of dealing with NAT or SIP ALG-related issues.
3. Ensure Devices Share Common Codecs
When you place a VoIP call, the two endpoints communicate and select a VoIP codec available to both devices. But if this process is unsuccessful, callers may experience one-way audio – as voice packets cannot be appropriately exchanged.
Incompatible Codec Solution
Make sure both endpoints support a common codec and that your line is set to the proper codec. Contact your provider with questions about correct codec names. For our users, use codec G.711 for all lines and SIP trunks. The United World Telecom network supports the G.711 codec, which provides the best VoIP call quality and uses no compression.
4. Reconfigure Routes
Network routing technology directs your call data from its source to its final destination. While your audio may successfully arrive at the endpoint, this doesn’t guarantee that you’ll always receive voice data in return. For example, If the call path from point A to B has a low-latency connection, but the data from point B to A takes a different path with high latency – you may experience one-way audio. These are both indications that routing misconfiguration may be present.
Routing Misconfiguration Solution
Many telecom professionals suggest troubleshooting this one-way audio issue using a “bottom-up” approach. This approach requires you to assess your IT infrastructure from the physical layer to software components to pinpoint where the misconfiguration is.
If you’re operating on a hosted VoIP service, this issue may lie on your provider’s side. So, work with your VoIP provider to diagnose the misconfiguration and fix the problem.
Solve Call Quality Issues with a Reliable Provider
With the right provider, you can avoid call quality issues altogether. And if they do come up, it’s vital that you solve them quickly. Look for a VoIP provider that understands your business communication needs and offers reliable services.
United World Telecom delivers high-quality hosted communications. We offer 24/7 support and a dedicated account manager for every user. This dedication helps avoid VoIP problems before they begin.
For more troubleshooting help or to learn more about our services, call us at 1 (877) 898 8646 or chat with us online!