Voice over IP (VoIP) continues to be an evolving force in the world of business communication, reshaping and improving how businesses communicate with their customers. But how do you get started with building a VoIP architecture that supports a cloud-based phone system?
We’ve created this guide that goes over core components, elements, and equipment to help businesses make informed decisions, ensuring their VoIP infrastructure aligns with their communication needs and demands.
In this extensive guide, we’ll cover the following essential topics:
- What is VoIP Architecture?
- Importance of Efficient Communication Architecture
- Switching to VoIP: Benefits + Features
- Key VoIP Call Components
- Planning Your VoIP Architecture: Best Practices + VoIP Diagrams
Let’s jump into it!
What is VoIP Architecture?
It is a network topology that determines how real-time audio will travel through your organization’s internet and infrastructure setup to enable VoIP calling.
Voice over IP is the process of converting analog voice signals into digital packets and transmitting them to the desired destination over the internet. This technology makes internet calling possible while reducing long-distance communication costs.
For this to occur effectively, VoIP functions and components typically include:
- Signaling: Needed for activation and operation of voice calls by allowing devices in the network to communicate with each other.
- Ability to connect and disconnect calls: Connecting endpoints and transmitting voice in real-time.
- Database services: Such as locating endpoints (and devices) via IP addresses, generating billing reports, and setting up security.
- VoIP codecs: Converting voice to digital packets to transmit via endpoints. You can adjust these codecs to meet different criteria for call quality.
We’ll dive more into different VoIP call components below.
Importance of Efficient Business Communication Architecture
Whether setting up a cloud communication system or connecting VoIP to PSTN, you need to consider how you want incoming and outgoing calls to travel within your network. While the concept of VoIP is simple enough, the actual VoIP architecture that makes it all possible is a little more complex. To experience clear and reliable VoIP service, a number of different components must work together seamlessly.
This can be especially challenging in enterprise VoIP environments where hundreds or even thousands of users make calls at the same time. That’s why it’s important for businesses to have a clear understanding of VoIP architecture.
Benefits of Switching to VoIP for Improved Communications
So, with complications and challenges present, why do we recommend you switch to VoIP nonetheless? Simply because these challenges have easy solutions and VoIP is worth the time spent creating a robust and reliable communication system.
Here are the key benefits of including VoIP in your communications architecture:
• Low upfront cost — VoIP works within your existing network, so you don’t need to buy additional equipment, hardware, or software.
• Low-cost calling — Plus, IP calling severely cuts down the costs of international and long-distance calling. So, your business can save on global sales and customer service calls.
• Easy setup and use — Cloud solutions are often easy to set up with minimal installation. Our cloud telephony solution, for example, takes only a few minutes to set up with no need for coding knowledge or an IT team. This also means that you don’t need an in-house IT team to manage and maintain your VoIP system.
• BYOD-friendly — Use your VoIP service from any device and location. This means teams can use their laptops, smartphones, tablets, and computers to make and receive business calls.
• Global connectivity — And, you can use your cloud phone service from anywhere in the world. This means you can connect your local, global, remote, and distributed teams through one phone network, increasing collaboration and operational efficiency. Plus you can use advanced routing rules to ensure incoming calls are routed to the right departments in the right locations.
• Business calling features — You also get access to enterprise-grade functionality with features like local and toll-free numbers, international call forwarding, call routing, dynamic caller ID, IVR/ACD, etc. View our list of VoIP features to get an idea of what such a service entails.
• Local presence — Use these features to build a local presence in target regions and increase call connection rates.
Key VoIP Features
VoIP phone systems can provide an array of features and functionality because of the various components that go into making this service possible. With location-flexibility and high-quality routing, you can expect these top features from most providers:
- Inbound and outbound call management
- IVR / ACD systems
- Advanced routing (time-based, location-based)
- Simultaneous routing
- International forwarding
- Call flow builder
- Voicemail
- Fax
- Caller ID management, and more.
Learn more about the advanced calling features United World Telecom offers.
VoIP Call Components
Now, let’s understand different call components—both hardware and software—that play a significant role in your VoIP architecture:
1. Signaling Gateway Controller (SGC)
The SGC is a translation device that passes call control information between dissimilar networks such as PSTN and IP-based networks. For VoIP architecture, this means establishing different endpoints and enabling functionality where one endpoint communicates with the other – also known as signaling. This gateway makes it easy to connect and translate calls between a PSTN and VoIP line.
The Signaling Gateway Controller is also known as a call agent for its call control functionality. And it also has a media gateway functionality that supports media control protocols such as H.248. This aside, the controller generates call detail records (CDRs), manages bandwidth policing, and provisions media connections.
2. Session Border Controller (SBC)
The SBC is a network component that secures VoIP and SIP-based networks. Typically, this controller is employed in enterprise VoIP infrastructures or networks sending and receiving business, fixed-line, or mobile VoIP services. The SBC is in charge of processing signaling messages and also handling all media traffic. They regulate and balance network traffic flow and manage bandwidth to ensure high performance.
3. Media Gateway
Media Gateways perform a few different functions to enable VoIP calling. The function of a specific gateway depends on your VoIP installation. They are primarily responsible for converting analog voice to digital packets and then transmitting these voice packets using RTP. And may even help with improving call quality through echo cancellation and silence suppression.
Now, if you have a converged PSTN-IP network — where it connects SIP trunks and POTS lines — then media gateways assist in the packetization (digitizing) of data. As such, it supports various trunking and compression algorithms as well as digital processing resources.
4. Media Server
Media servers enable added media-related features like voicemail, IVR, special tones, messages or announcements, voicemail-to-email, call recording, voice-based dialing, and so on. Servers are built to handle hundreds of SIP and VoIP calls occurring simultaneously. This way, they allow you to place and manage multiple calls at the same time.
5. Application Server
Application servers, on the other hand, power applications within your system such as call forwarding, call transfer, call detail records (CDRs), etc. These servers typically work alongside media servers and session controllers to enhance feature functionality.
6. Database Services
Databases record and store important registration details of all SIP devices as well as call logs and history.
7. SIP Services
Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is an IP that manages the connection and disconnection calls between two endpoints. Because of this capability, SIP plays a significant role in the transmission of voice, video, and messaging across the internet.
8. Cloud PBX
A cloud PBX is an IP-enabled PBX that businesses can use as a control center for their communication systems. The PBX uses SIP trunkings for voice transmissions and it comes with other core telephony features such as IVR, routing, extensions, etc.
9. Endpoint Devices
These are your VoIP devices or devices you use to make and receive VoIP calls. These include IP phones, computers, laptops, softphones, fax machines, etc., that work with your VoIP phone service.
10. IP Network
An IP network connects multiple computers and devices via their specific internet protocol (IP) addresses. This allows users within this network to securely send and share information between established endpoints.
11. VoIP Codecs
To ensure high-quality audio during calls, codecs convert analog signals into digital packets in various degrees of compression. The best codecs for HD VoIP calls are G.711, G.722, and G.729.
Planning Your VoIP Architecture: Best Practices
When deciding how you want to set up VoIP within your business, you will need to keep in mind:
- Business calling needs
- VoIP call components
- VoIP network diagrams
- Bandwidth required for VoIP calling
- VoIP phone services
- Budget and resources
1. Determine Communication Needs
Start by understanding your existing setup and future expansion goals. In other words, what you need to support your business’ current communication needs, and what you may need to help the business grow and scale. The first step to planning your VoIP architecture is to determine your call needs. Consider these questions:
- How many employees do I need to support now?
- Where are my employees and customers located?
- What kind of phone and network coverage will I need?
- Do I have to support local, remote, global, and/or distributed teams?
- Where will the organization be in 1-2 years? What communication needs might arise then?
- Are there any problems we can solve with our new architecture? (new software, advanced routing, etc)
- What VoIP features and functionalities will help teams be more productive and efficient?
- What remote tools will my teams need access to?
Once you have answered these questions, you can start to identify providers and solutions that can help you achieve your goals.
Similarly, you’ll need to decide if you want to go fully cloud-based or simply upgrade your in-house PBX system with a SIP trunking service.
Related: Cloud PBX vs On-Premises PBX: Which is Right for Your Business?
2. Determine Bandwidth Requirements
This is an important step because if you don’t plan for bandwidth capacity in advance, call quality and connection will be affected. From what you receive from your ISP, you’ll need to set aside a chunk of bandwidth specifically for VoIP. Otherwise, your calls will compete with other internet activity, leading to lower quality.
To decide how much bandwidth you’ll need, consider the number of employees making calls simultaneously. Here’s a quick reference guide:
| Number of Concurrent Calls | Bandwidth Recommended |
| 1 | 100 Kbps |
| 5 | 500 Kbps |
| 10 | 1 Mbps |
| 15 | 1.5 Mbps |
| 20 | 20 Mbps |
Since VoIP calls require high-speed internet at all times, you want to make sure your ISP can support your VoIP service. This means contacting your ISP and VoIP providers and ensuring both services are compatible with your internet requirements.
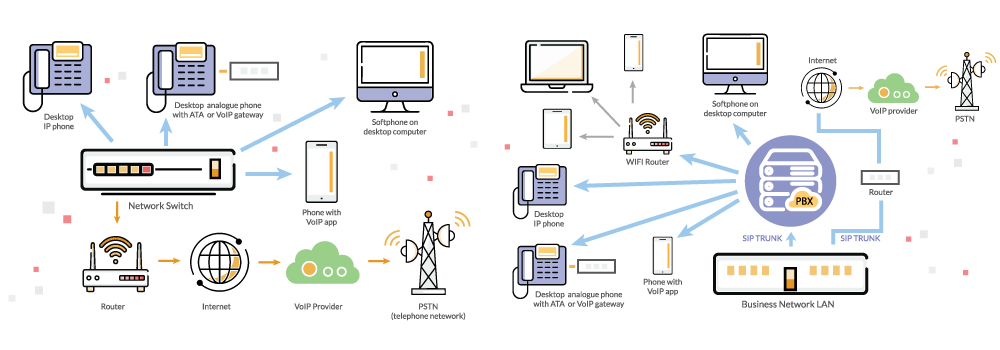
3. Use VoIP Diagrams
Deciding which VoIP components and features are significant and how to place them in your infrastructure can be overwhelming. This is where VoIP diagrams come in handy. But first, what is a VoIP diagram?
VoIP diagrams help you decide how many endpoints you need to cover, what each endpoint needs, and how to connect all these different functioning parts together.
Here are some examples of VoIP diagrams to help you build your internal architecture:
Still not sure what’s the right setup for your business? Our telecom experts can help you out! Chat with one of us today.
4. Get Reliable VoIP Services
Once you have an idea of how to set up your VoIP phone system, you’ll need to subscribe to a VoIP service. Take time to research and identify the right VoIP provider to meet your needs and budget.
- When researching or changing VoIP providers, look for a provider who:
- Has a variety of calling features,
- Is compatible with your existing infrastructure,
- Supports your forwarding and routing needs,
- Covers your local, remote, and global teams,
- Meets your communication budget and is scalable, and
- Does not require additional fees or long-term commitments.
Most providers offer a free trial or demo to see how their service works in action. Try these out to get a feel for the service’s usability and interface. Once you’ve decided on the provider, you can set up your new phone system and train employees on how to use it.
We recommend businesses avoid using multiple VoIP providers as that situation can quickly become complicated. For instance, your architecture needs to comfortably integrate multiple providers and their products, which is hard to do. Additionally, when a crisis hits, it can prove difficult to identify the source of a technical issue and troubleshoot it. On top of that, your teams are tasked with juggling multiple contracts, regulations, and agreements. Working with only one global provider can simplify your processes and increase efficiency.
5. Plan Network Monitoring & Security
As with any new product, conduct regular checks to ensure your VoIP architecture is working as desired. It helps to decide how your teams will do this beforehand so you don’t waste crucial time later. This especially helps in disaster recovery.
Typically, a VoIP network requires constant monitoring; this can be done on both the provider and your end. Since VoIP is cloud-based and hosted, your provider will have network monitoring protocols in place to ensure calls are routing smoothly and without interruption. On your end, you’ll want to ensure your system meets essential VoIP requirements such as enabling QoS settings, checking uptime, running speed tests, and more.
Use our VoIP troubleshooting guide to determine and resolve common VoIP problems that can affect call quality.
Part of network monitoring is ensuring security is set in place and protecting your systems as required. As internet-dependent, VoIP systems are prone to issues like attacks on the network, viruses, remote eavesdropping, and so on. This means watching for cyber-attacks and data breaches and planning in advance how to tackle them. Common security best practices include:
- Routinely changing and implementing strong passwords
- Encrypting WiFi or using a secure VPN
- Enabling network address translation (NAT) when required
- Keep systems and equipment up to date
- Educating employees on security measures, and so on.
To learn more, check out our guide to VoIP security.
Adding United World Telecom as Your VoIP Provider
Building your business’ VoIP phone system can seem overwhelming; after all, you need to efficiently fit multiple pieces together. That’s where a professional VoIP service can support you.
For over 27 years now, we, at United World Telecom, have been assisting businesses and enterprises set up their VoIP phone service. From supplying you with VoIP services to responsively troubleshooting any issues that come up, you can rely on our 24/7 support team and telecom experts.
Want to see our service in action? Book a demo today! Call us at 1 (877) 898 8646 or chat with us online! We’re here to help!