Given that voice calls still hold a pivotal role in customer service, ensuring call quality is paramount for customer satisfaction. Which is why dropped calls can be incredibly frustrating, especially when you are in the middle of an important business communication. These untimely termination of calls can easily result in the loss of valuable customers.
And yet call drops remain a common VoIP issue.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of dropped VoIP calls, their causes, and effective troubleshooting methods.
What is a Dropped Call?
For instance, imagine you’re on a business phone call while driving, and as you enter an area with a weak or no signal, your call gets disconnected. In this case, the call drops because your phone loses connection to the cellular network.
Dropped VoIP calls, on the other hand, happen due to a variety of other reasons from poor internet connection to defective equipment.
Impact of Dropped Calls
Reliable communication is a cornerstone of business effectiveness and customer satisfaction. And therefore, the impact of dropped calls can be far-reaching. Here’s how it can affect your business:
- You could lose a crucial sales opportunity or miss an important business discussion, resulting in potential revenue loss.
- Dropped calls can not only frustrate your customer but also drive them toward competitors, jeopardizing your customer base.
- Persistent call drops can tarnish your brand image, damaging the reputation of your business.
- The burden of dealing with angry customers could take an emotional toll on your agents, adversely affecting their morale and, consequently, overall productivity.
6 Causes of Dropped Calls
Numerous factors can lead to call drops, such as poor signal strength, interference, network congestion, and technical glitches. In these scenarios, the phone system struggles to maintain a stable connection between the callers, resulting in an abrupt call termination.
Let’s look at the common causes of dropped VoIP calls:
1. Inadequate Network Capacity
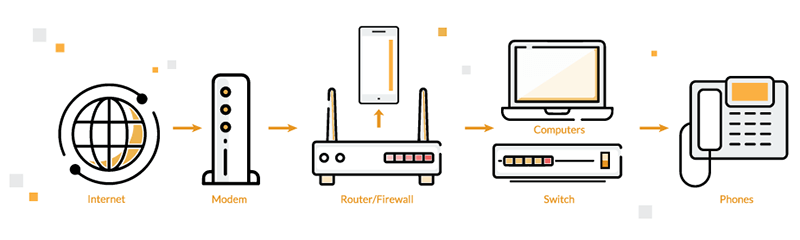
Dropped VoIP calls happen when your internet speed isn’t up to the task, especially with voice and video calling. This can result in network congestion and data loss, making your calls sound garbled or cutting it off completely. When your network is overloaded or doesn’t prioritize calls, then too you might face call drops. In case of mobile calls, weak signals or congested areas can lead to dropped calls; same goes for weak or disrupted Wi-Fi signals.
Related: Guide to VoIP Network Requirements
2. Loss of Signal
In VoIP calls, your voice becomes digital data sent over the internet in real-time. So if the signal weakens or disappears, it’s like losing bars during a regular call. This can result in issues like delays and dropouts. And if the signal worsens significantly, you might lose the call altogether. VoIP relies on a steady and consistent internet connection to function properly.
3. Connection Time Limit
Sometimes VoIP service providers set time limits for each call session, typically based on the user datagram protocol (UDP) timeout value. Providers put this cap or limit on to protect users from excessive billing charges or avoid line congestions. If your call goes beyond the allowed time, the session could end abruptly. Problems also arise due to session initiation protocol (SIP) timers, misconfigured or faulty on your router.
4. Hardware or Software Issue
If the device you’re using, like a phone or computer, encounters technical problems, it can lead to sudden call drops. Similarly, if your networking device, such as a router, isn’t working properly or is physically damaged, it can weaken your internet, making it unsuitable for clear phone calls. The same goes for using outdated software.
5. Audio Detection Problems
When your system or microphone malfunctions, your voice may not get transmitted or received correctly, leading to call terminations. This situation can be likened to the other person suddenly losing the ability to hear you in a traditional phone call due to microphone issues.
For instance, when your microphone malfunctions, your voice may not get transmitted or received correctly. And when audio is not detected, the VoIP system may view it as a failed call and therefore, drop it.
6. Environmental Reasons
Environmental factors like interference from other devices, power outages, bad weather, and maintenance work can also mess up phone signals, causing calls to drop. While these external factors are typically not in your control, you should try and limit them as much as possible. For example:
- Avoid scheduling business calls during maintenance work
- Set up redundancy routing and failover forwarding as a backup
- Reduce use of other devices during work hours, and so on.
Related: How to Achieve the Best VoIP Call Quality for Your Business?
How to Troubleshoot Dropped VoIP Calls: 5 Fixes
When it comes to tackling the frustrating problem of dropped VoIP calls, we’ve got you covered. From optimizing your VoIP network settings to fixing malfunctioning devices, there are practical solutions that can make a big difference.
1. Improve Network Bandwidth, Internet Plan, and Signal Reception
To begin, assess your internet capabilities using online speed testing tools. Check upload and download speeds and jitter times. Switch to a wired or ethernet connection for stable connectivity. Consider upgrading to a faster internet plan for improved call quality. Optimize your Wi-Fi signal by relocating your router to a more central spot in your home.
Also, consider closing or disabling unnecessary apps that might be consuming too much internet bandwidth and potentially causing call disruptions. And using VoIP QoS settings to prioritize traffic over your network.
Watch this video to learn more about VoIP Quality of Service (QoS) and addressing quality issues:
2. Increase Session Time
Extend the duration of your calls without interruptions by tweaking your internet settings. Examine your VoIP settings to increase session time. You can also contact your VoIP and internet telephony service provider (ITSP) to eliminate or extend time limits for each call session. If the timer runs out, the system assumes your call is over and ends the session, so adjusting these settings can prove quite helpful.
3. Check Hardware and Internal Issues, Use Proper Functioning Hardware
Ensure your devices and software are correctly set up, and keep them up to date by installing updates. Confirm that all hardware is in good working order, and replace or repair any malfunctioning components that might be causing call drops. Check for loose cables and ensure secure connections. Try rebooting your router by turning it off, waiting a few minutes, and then turning it back on. Additionally, don’t forget to have your mobile SIM card checked for issues.
4. RTP Adjustments
Real-time transport protocol (RTP) is like a set of rules for sending live audio and video over the internet. It’s essential for smooth internet phone calls, video chats, and more. RTP silence detection can be overly sensitive, causing call drops. Adjust or disable silence detection settings in your VoIP application or device.
5. Contact Internet and VoIP Service Providers
Lastly, if you’ve tried the previous tips and call drops persist, reach out to your internet service provider (ISP). They can conduct diagnostics to ensure that your internet connection is stable and suitable for VoIP calls. Your ISP can help address any underlying network issues that may affect your call quality.
If the problem persists, it could be because of network infrastructure, technical support, or inadequate service quality that your current VoIP service provider cannot address. So it may be time to change VoIP providers! A good service provider offers consistent call quality and support.
How Can UWT Help?
As you know, one cannot understate the significance of dropped VoIP calls. And so it is vital to partner with a reliable VoIP service provider like United World Telecom for clear and uninterrupted call connections. With a proven track record of delivering high-quality VoIP service since 1996, we are well-equipped to address all your queries related to VoIP calls.
Don’t let dropped calls hold you back. Speak with our in-house experts to upgrade your business communications system. Contact us now!