When researching business phone service or VoIP providers, you will come across the term CTI or computer telephony integration. Here we explain what computer telephony integration or CTI software is and how businesses can use this technology to streamline business communication and increase agent productivity.
Computer Telephony Integration: What is CTI Software?
In simple terms, CTI is a technology that connects computers and telephony. Computer telephony integration or CTI technology enables computers to interact with telephones or perform telephone functions like placing and routing calls.
A CTI software is designed to streamline contact center operations and improve agent performance and productivity. Mostly used in call centers, CTI software can also be used in businesses of various sizes that have a steady stream of call traffic.
CTI Functions
So, what can your business use computer telephony integration for? There are many functions for CTI technology — here are some ways to use this technology:
- Make phone calls from your computer at the click of a button.
- Identify callers by matching the incoming phone number to a database of customer records.
- Route and transfer calls through advanced routing and self-service options such as IVR.
- Display customer information on agents’ screens before they take the call, also known as screen popping.
- Access to call logs, reporting, and recording functions.
- Access to manual and automatic dialing options such as click-to-call, autodialers, and softphones.
- Conduct basic phone controls such as answer, transfer, conference, hold, etc.
Computer Telephony Integration Applications
What are some common applications of computer telephony integration technology and what businesses can take advantage of this software? Some computer telephony integration applications include:
- Call and contact centers
- Business with distributed teams and remote employees
- Business process outsourcing (BPO)
- Small-to-large businesses with high call traffic (fluctuating and consistent)
- Businesses with multiple offices and customer service locations spread geographically
- Companies with global coverage and international clientele

5 Benefits of Using CTI Software for Business Communication
How can your business use CTI and benefit from this type of VoIP integration?
1. Place Calls With Any Device
The main attraction and benefit of using CTI software is that users do not need telephones or desk phones to make and receive business calls. Instead, they can simply click to call through their computers or laptops using headsets. This helps cut down costs on additional equipment needed.
2. Caller Authentication Through Integrations
Computer telephony integration technology easily integrates with most CRMs, further simplifying and streamlining agent processes. The CTI preemptively identifies the caller by screening the phone number or email address through the customer database and then displaying the information on the agent’s computer screen. This is also known as screen popping or screen pop. By automatically authenticating the customer, the agent is prepared to offer fast service.
Additionally, depending on the type of CRM used, call records may be automatically added to the customer’s record for data analysis in your call center. Think: call history, call detail records, transcripts, metrics, and other important caller information.
3. Advanced Call Routing Options
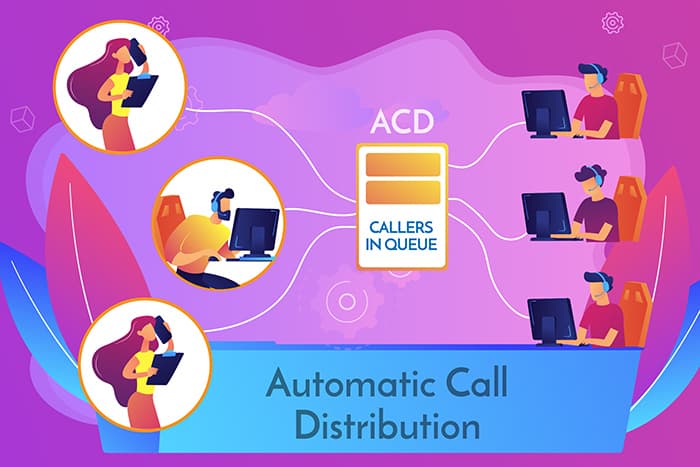
Another key feature of CTI software is providing call routing and transfer. With computer telephony integration technology, your business can route and manage calls more effectively. You can use an interactive voice response system or automatic call distributor to route calls automatically based on predetermined rules.
To do this, design and create an easy-to-use and informative IVR system. When callers call your business, they will be presented with menu options and prompted to speak or push buttons for further options or to be transferred to the right department. Based on their input, they will be assisted or transferred to the appropriate department. Some ways to route calls include:
- Caller input — Callers indicate what they need through the IVR menu
- Caller history — Based on the caller’s previous interactions with the business
- Agent availability — Routes to the next available agent or employee
- Location-based routing — Based on the location of the caller
- Time-based routing — Based on the time of day of the call
- Skill-based routing — Based on the skill or expertise needed (for example, language preferences)
- Department needed — Callers indicate what department they need
These call routing options help with call management so your callers get to the right agent and receive assistance as quickly as possible. You can reduce wait times and frustration related to being routed to the wrong person or department.
4. Collaboration Tools
Besides making it easy for customers to connect with your business, CTI technology also supports in-house collaboration through:
- Voice and video conferencing
- Call whisper and call barging
- Warm call transfer
- Call monitoring
- Call recording
With these training and collaboration tools, teams can work together and managers or supervisors can listen in on calls and provide coaching.
5. Unified Communication Tools
Finally, along with phone calls, CTI software can also be used to receive faxes and emails. This makes it a UCaaS trend that lets you access all you need about a customer and their history with your company.
Want to Learn More About Advanced Telephony?
Our telecom experts can help you find the right business communication set-up for your company. Call us at 1 (877) 898 8646 or chat with us online to learn more!